The role of structured cabling in industrial environments: Addressing modern challenges
From manufacturing plants and logistics hubs to oil refineries and transportation networks, structured cabling plays a pivotal role in supporting automation, data transmission, and communication.
However, the demanding conditions of industrial environments call for specialized solutions that go beyond traditional cabling systems. By understanding key standards like TIA-1005-A and the importance of MICE classifications, organizations can deploy robust and future-ready infrastructures.
Among the solutions addressing these challenges, ruggedized products such as DINTEK's IP67 DuraMAX line provide an example of how tailored cabling can support industrial-grade performance.
Industrial standards: TIA-1005-A and MICE classifications
The TIA-1005-A standard is a cornerstone for designing telecommunications cabling in industrial environments. It establishes guidelines that consider the unique demands of these settings, such as exposure to vibration, dust, temperature extremes, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Central to this standard is the MICE model, which classifies environments based on four key factors:
Mechanical (M)
Risks of physical impact, vibration, and tension
Ingress (I)
Potential exposure to dust, water, or other contaminants.
Climatic (C)
Variations in temperature, humidity, or other environmental factors.
Electromagnetic (E)
Susceptibility to electromagnetic interference from industrial equipment.
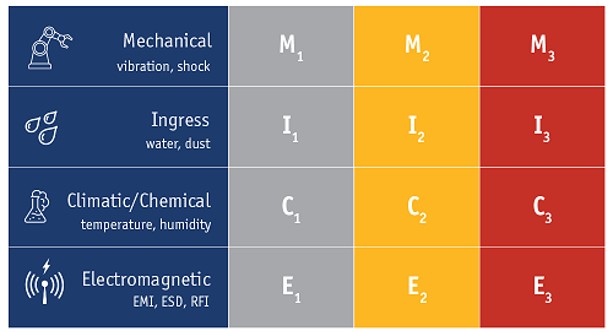
These classifications are broken down into three categories:
MICE 1: Controlled environments, such as offices or clean rooms.
MICE 2: Moderately harsh conditions, with occasional exposure to stressors.
MICE 3: Severe conditions, characterized by constant or high levels of mechanical, ingress, climatic, and electromagnetic challenges.
Understanding the MICE model allows organizations to select the appropriate cabling for each zone, ensuring reliability and performance in diverse conditions.
The role of Cat.6 cabling in industrial networks
Category 6 (Cat.6) cables are widely used in industrial environments due to their high-speed performance and robustness. Designed to handle data transmission rates of up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances, Cat.6 cables are ideal for machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, real-time monitoring, and other bandwidth-intensive applications.
Why Cat.6 works well in industrial settings
Minimized crosstalk: Tighter twists and superior shielding reduce EMI, which is particularly valuable in MICE 2 and MICE 3 environments.
High-speed data transmission: Cat.6 supports fast and reliable communication, essential for industrial automation and data processing.
Durability: Enhanced physical construction ensures the cables can withstand moderate mechanical stress and temperature variations.
When combined with ruggedized components, such as IP67-rated connectors, Cat.6 cabling becomes a powerful tool for establishing reliable networks in harsh industrial conditions. Products like DINTEK’s IP67 DuraMAX range exemplify this combination, offering extra layers of protection to meet stringent industrial demands.
The growing role of fiber optics
While copper cabling like Cat.6 is invaluable, fiber optics has emerged as a critical component in industrial networks. Fiber optics excel in scenarios requiring high bandwidth and immunity to EMI, making them especially useful in facilities with extensive machinery and electrical equipment.
Key benefits of fiber optics in industrial applications
Bandwidth and Speed: Fiber optics can handle significantly larger data volumes at faster speeds, catering to the increasing demands of Industry 4.0.
Distance: Unlike copper, fiber optic cables maintain signal integrity over much longer distances, which is essential in sprawling industrial complexes.
Resistance to Environmental Stress: Immune to EMI and less affected by temperature changes, fiber optics perform reliably in challenging conditions.
Hybrid systems that combine copper and fiber optics are becoming more prevalent, offering the flexibility to balance cost, performance, and durability. For example, fiber backbones paired with Cat.6 connections to endpoint devices create a network that is both resilient and efficient.
Designing for industrial environments
The success of an industrial network hinges on careful planning and adherence to established standards like TIA-1005-A. DINTEK’s DuraMAX IP67 Industrial Cabling products offer pre-tested, reliable options for industrial environments, making the deployment process simpler and more secure.
Environmental Analysis
Assess the MICE classification of the area to determine the appropriate cabling requirements.
Future proofing
Invest in high-performance solutions like Cat.6 or fiber optics to accommodate growing data demands.
Segmentation & zoning
Divide the network into manageable zones, reducing complexity and improving fault tolerance.
Ruggedized components
Use IP67-rated connectors, enclosures, and cables for areas exposed to harsh environmental factors.
Conclusion
Structured cabling plays a vital role in industrial environments, ensuring seamless communication and automation in the face of demanding conditions. By following industry standards such as TIA-1005-A and incorporating MICE classifications, businesses can build resilient networks capable of withstanding physical stress, environmental challenges, and electromagnetic interference.
High-performance solutions, including Cat.6 cables and fiber optics, serve as the backbone of these systems, delivering speed and durability. Innovative products like DINTEK’s IP67 DuraMAX range demonstrate how cabling can be designed to excel in harsh industrial settings.
With growing data needs and evolving technologies, implementing scalable and durable cabling infrastructure is crucial for optimizing efficiency and future-proofing operations.








